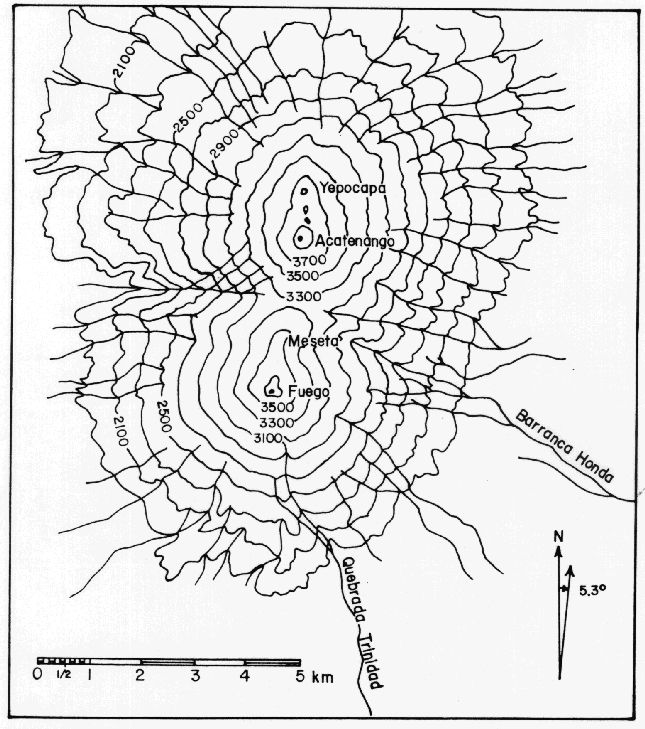
The map above is a simple topographic map of the Fuego and Acatenango volcanic complexes in Guatemala. Fuego is one of Guatemala's 4 active volcanoes.
The circular rings (contour lines) illustrate the increasing elevation of each volcanic peak. The largest outer ring indicates the base of the volcano, with each progressive ring illustrating a higher elevation up the mountain, until reaching the volcano's peak (the smallest ring, with highest elevation).
http://www.geo.mtu.edu/volcanoes/fuego/pic/f29.gif

No comments:
Post a Comment